ECS (Elastic Container Service)
- ECS = Elastic Container Service
- Launch Docker containers on AWS
- You must provision & maintain the infrastructure (the EC2 instances)
- AWS takes care of starting / stopping containers
- Has integrations with the Application Load Balancer
Launch Types
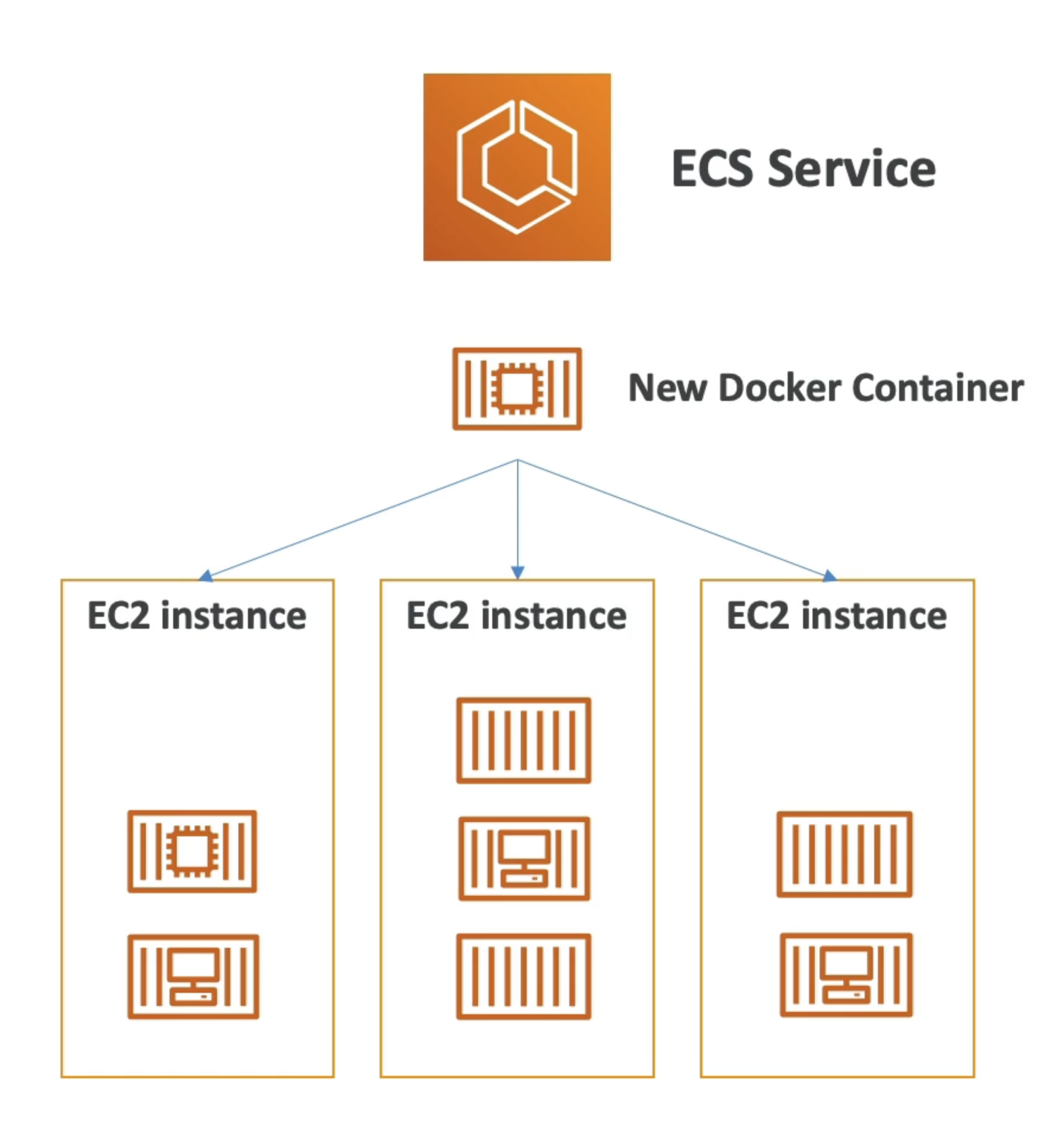
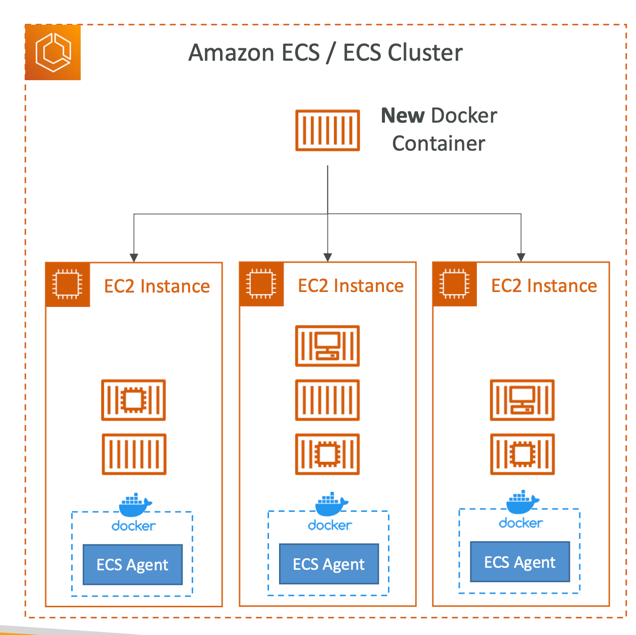
EC2 Launch Type
- Launch Docker containers on AWS = Launch ECS Tasks on ECS Clusters
- EC2 Launch Type: you must provision & maintain the infrastructure (the EC2 instances)
- Each EC2 Instance must run the ECS Agent to register in the ECS Cluster
- AWS takes care of starting / stopping containers
Fargate Launch Type
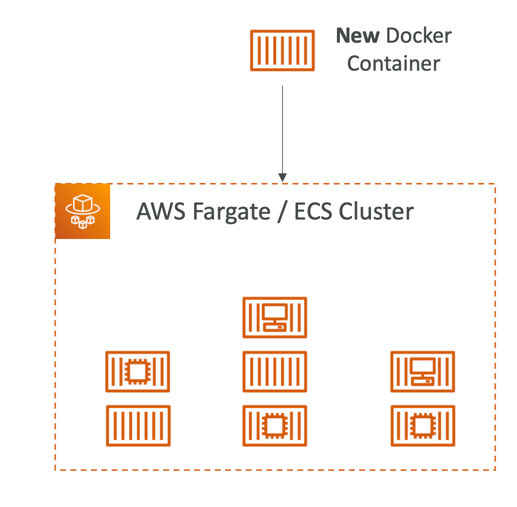
- Launch Docker containers on AWS
- You do not provision the infrastructure(no EC2 instances to manage)
- It’s all Serverless!
- You just create task definitions
- AWS just runs ECS Tasks for you based on the CPU / RAM you need
- To scale, just increase the number of tasks. Simple - no more EC2 instances
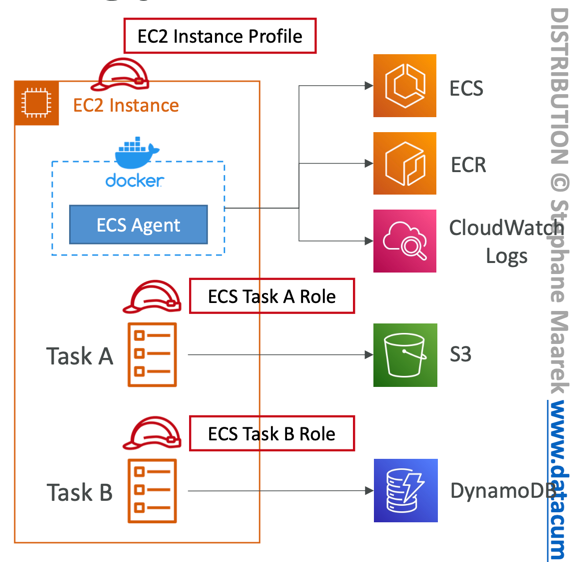
IAM Roles for ECS
- EC2 Instance Profile (EC2 Launch Type only):
- Used by the ECS agent
- Makes API calls to ECS service
- Send container logs to CloudWatch Logs
- Pull Docker image from ECR
- Reference sensitive data in Secrets Manager or SSM Parameter Store
- ECS Task Role:
- Allows each task to have a specific role
- Use different roles for the different ECS Services you run
- Task Role is defined in the task definition
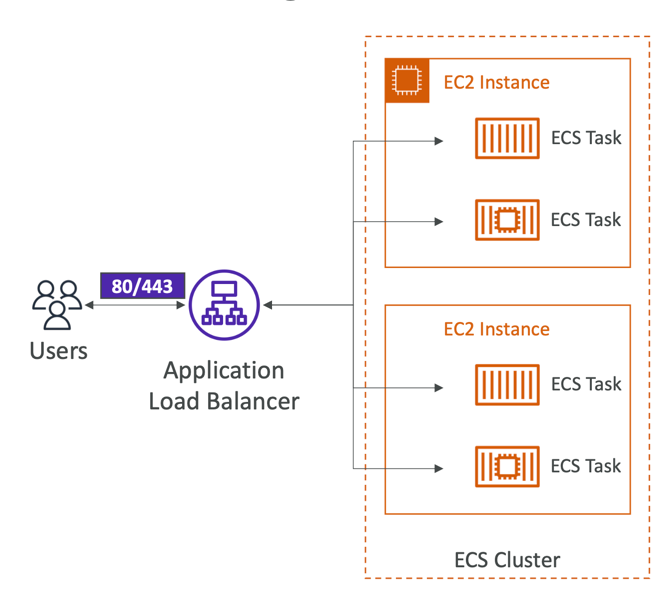
Load Balancing Integration
- Application Load Balancer supported and works for most use cases
- Network Load Balancer recommended only for high throughput / high performance use cases, or to pair it with AWS Private Link
- Classic Load Balancer supported but not recommended (no advanced features - no Fargate)
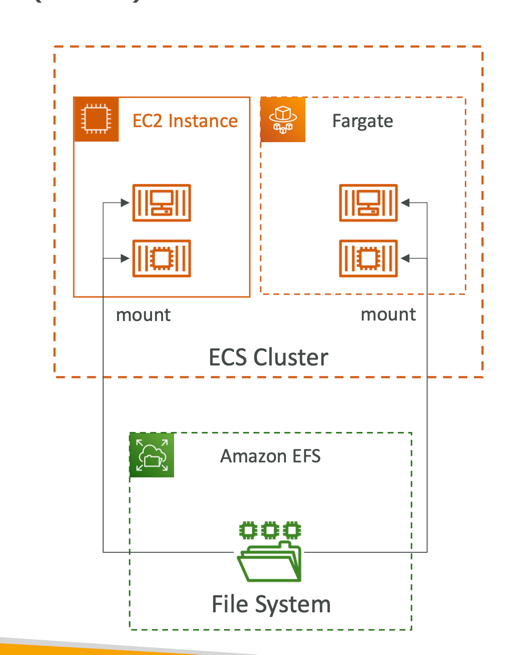
Data Volumes
- Mount EFS file systems onto ECS tasks
- Works for both EC2 and Fargate launch types
- Tasks running in any AZ will share the same data in the EFS file system
- Fargate + EFS = Serverless
- Use cases: persistent multi-AZ shared storage for your containers
- Note:
- Amazon S3 cannot be mounted as a file system
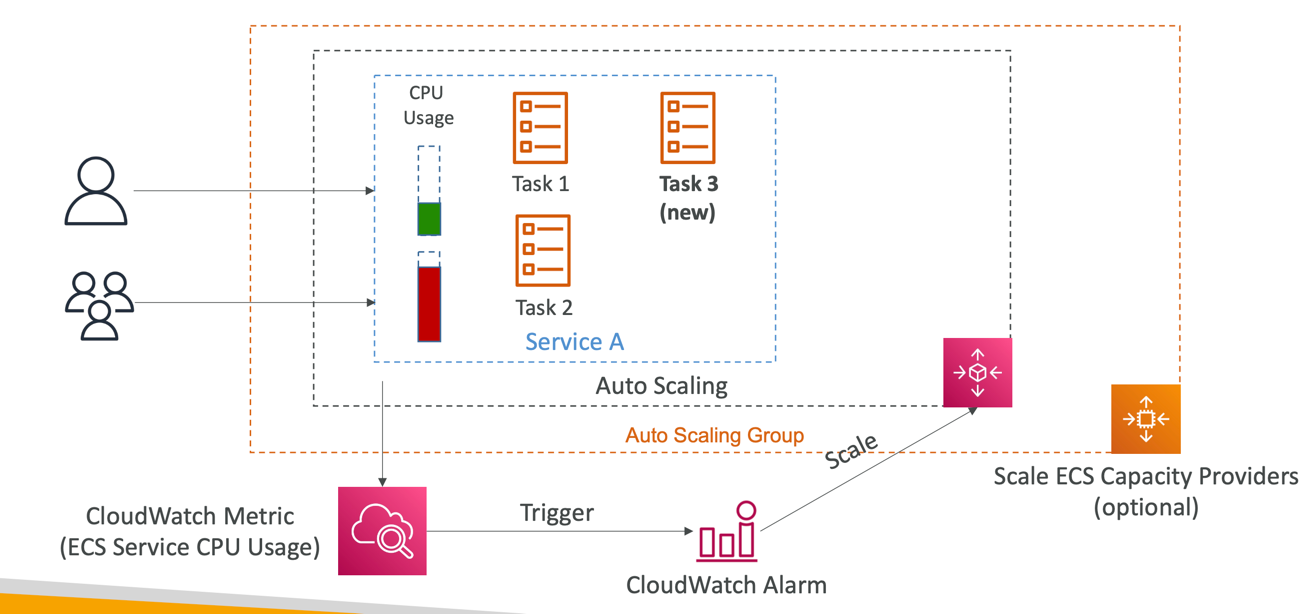
ECS Service Auto Scaling
- Automatically increase/decrease the desired number of ECS tasks
- Amazon ECS Auto Scaling uses AWS Application Auto Scaling
- ECS Service Average CPU Utilization
- ECS Service Average Memory Utilization - Scale on RAM
- ALB Request Count Per Target – metric coming from the ALB
- Target Tracking – scale based on target value for a specific CloudWatch metric
- Step Scaling – scale based on a specified CloudWatch Alarm
- Scheduled Scaling – scale based on a specified date/time (predictable changes)
- ECS Service Auto Scaling (task level) ≠ EC2 Auto Scaling (EC2 instance level)
- Fargate Auto Scaling is much easier to setup (because Serverless)
EC2 Launch Type – Auto Scaling EC2 Instances
- Accommodate ECS Service Scaling by adding underlying EC2 Instances
- Auto Scaling Group Scaling
- Scale your ASG based on CPU Utilization
- Add EC2 instances over time
- ECS Cluster Capacity Provider
- Used to automatically provision and scale the infrastructure for your ECS Tasks
- Capacity Provider paired with an Auto Scaling Group
- Add EC2 Instances when you’re missing capacity (CPU, RAM…)
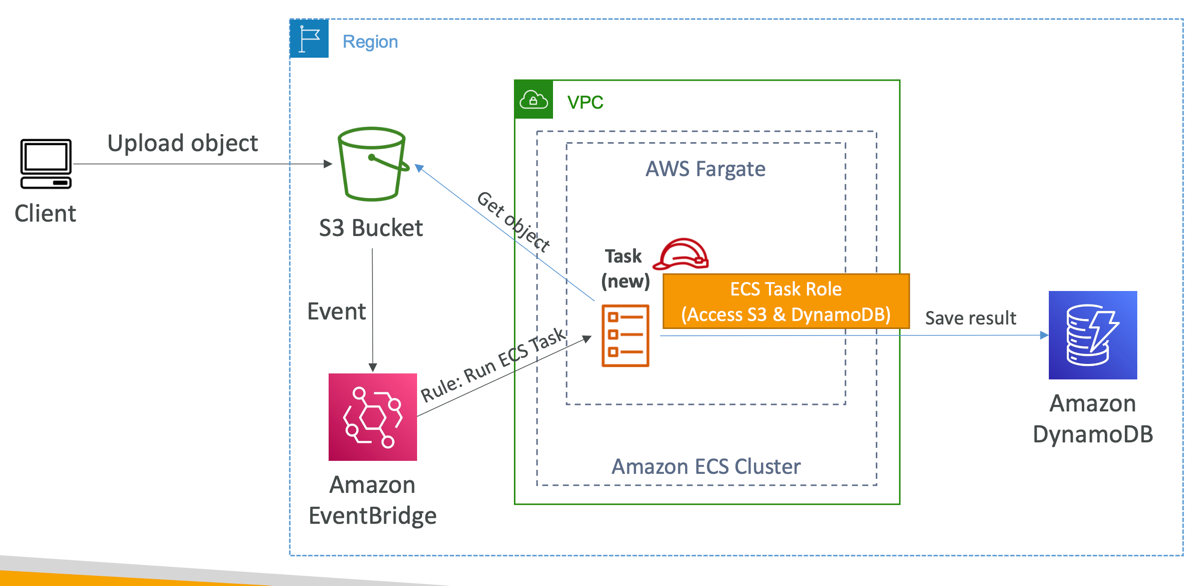
ECS tasks invoked by Event Bridge